√70以上 club fungi examples 157363-Club fungi examples
Basidiomycota are typically filamentous fungi composed of hyphae Most species reproduce sexually with a clubshaped sporebearing organ ( basidium) that usually produces four sexual spores (basidiospores) Basidia are borne on fruiting bodies (basidiocarps), which are large and conspicuous in all but the yeasts, rusts, and smutsThe division of fungi known as the club fungi, Basidiomycota, includes some of the most familiar fungi Mushrooms, puffballs, and shelf fungi are all members of• Zygote fungi • Sac fungi • Club fungi • Imperfect fungi • Lichens Zygote fungi • Zygomycetes • Rhizopus bread mold Examples Mycorrhizae • Fungal roots • Hyphae grow into root • Help to deliver nutrients to the plant • Fungus gets sugar and other molecules
Club Fungi King Of Kingdoms
Club fungi examples
Club fungi examples-A feature is sexual spores in sacs (asci);Sac fungi are those which belongs to Ascomycota division or phylum of the kingdom fungi These fungi produce ascospores (which are sexual spores) in sac like structures known as asci (singular ascus) Some examples of sac fungi are as follows 1




Mushroom Definition Characteristics Species Facts Britannica
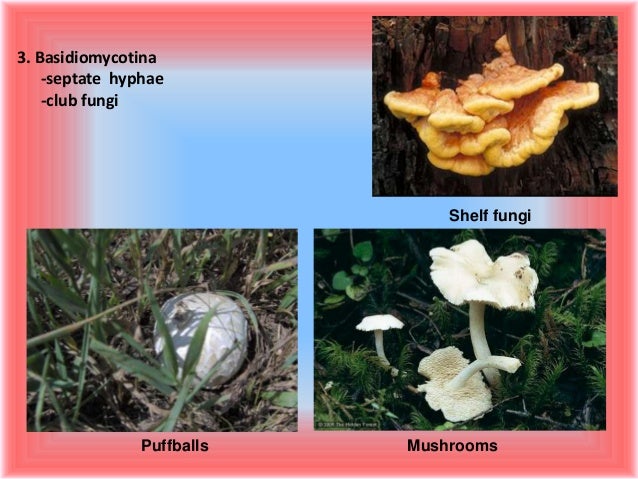
Basidiomycetes – The Club Fungi 1 Basidiomycetes (Gk basidium small base, mykes fungus) are the most advanced and most commonly seen fungi as their fructifications are often large and conspicuous, eg, mushrooms (gill fungi), toadstools, puff balls, bracket fungi, etcSome examples are Alternaria, Colletotrichum, and Trichoderma Basidiomycetes are Commonly known as club fungi and known forms are mushrooms, bracket fungi or puffballs Ascomycetes are Commonly known as sacfungi, the ascomycetes are mostly multicellular, eg, Penicillium, or rarely unicellular, eg, yeast (Saccharomyces) M ushroom s , puffballs , stinkhorn s , bracket fungi , other polypores ,
Ascomycota (sac fungi) may have unicellular or multicellular body structure;Club fungi examples mushrooms, birds nest fungi, puffballs sac fungi examples morels, truffles, yeast bread mold is an example of what phyla zygomycota symbiotic relationship fungus lives off of anther organism but the fungus will give something back Mycrorrhizae1 symbiotic relationshipExamples include the yeasts used in bread, wine, and beer production Basidiomycota (club fungi) have multicellular bodies;
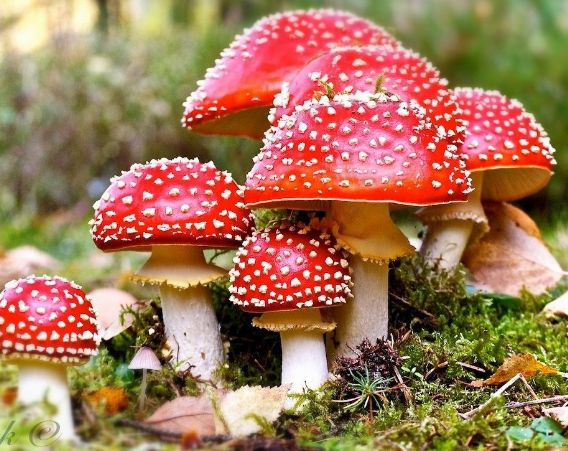
Basidiomycota a taxonomic division within the kingdom Fungi 30,000 species of fungi that produce spores from a basidium basidium a small structure, shaped like a club, found in the Basidiomycota phylum of fungi, that bears four spores at the tips of small projections basidiospore a sexuallyreproductive spore produced by fungi of theClub fungi are important as commercial crops They also cause many diseases that result in loss or reduction of grain yields Agaricus bisporis is the common mushroom found in grocery stores as the white button mushroom, crimini mushroom, and the fabulous portabella mushroomLentinus edodes is the less commonly bought shitake mushroom (in my hobbitsh mushroom loving mid a tastyFeatures includes sexual spores in the basidiocarp (mushroom) and that they are mostly decomposers;




What Is A Disease




The Vegetable Caterpillar An Intriguing Fungus Karen Retra
Fungi are eukaryotic, like protists Habitat Club fungi live on dead and decaying plant matter What They Eat Club fungi's enzymes decompose wood, leaves, and other organic materials What Eats Them Mobility Club fungi can reproduce asexually, but sexual reproduction is more common ExamplesADVERTISEMENTS The following points highlight the top eleven features of basidiomycetes 1 The somatic phase consists of a welldeveloped, septate, filamentous mycelium which passes chiefly through two stages (a) Primary mycelium ADVERTISEMENTS It is formed by the germination of a basidiospore and contains a single haploid (n) nucleus in each cell It bears neither sex An example of Fungi You know 6 Mushrooms – "Club Like" Fungi or Basidiomycete Fungi 7 Bracket Fungi – Basidiomycete Fungi 8 Bread Mold – a Zygomycete Fungi 9 Cup Fungi – Ascomycete Fungi Note the cup shapes and orange peel colour 10



1




The Kingdom Of Fungi Amazon Co Uk Petersen Jens H Books
The common members are edible mushrooms ( Agaricus ), smut ( Ustilago) and rust ( Puccinia ) (5) Deuteromycetes (Fungi imperfecti) The group include all those fungi in which sexual or perfect stage is not known Mycelium is made of septate hyphaeClub fungi can reproduce asexually, but sexual reproduction is more common They reproduce using spores Development Sac fungi grow hyphae from the spore The mycelia have a huge surface area Examples Some examples of club fungi include mushrooms, polypores, puffballs, boletes, and bird's nest fungi Saprophytic – The fungi obtain their nutrition by feeding on dead organic substances Examples Rhizopus, Penicillium and Aspergillus Parasitic – The fungi obtain their nutrition by living on other living organisms (plants or animals) and absorb nutrients from their host Examples Taphrina and Puccinia




Characteristics Of Fungi Biology For Non Majors Ii



Biology4kids Com Microorganisms Fungi
Examples include the yeasts used in bread, wine, and beer production Basidiomycota (club fungi) have multicellular bodies;Learning Outcomes Identify characteristics and examples of fungi in the phylum Basidiomycota Figure 1 The fruiting bodies of a basidiomycete form a ring in a meadow, commonly called "fairy ring" (Credit "Cropcircles"/Wikipedia Commons) The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia Example of Ascomycetes (Sac fungi) Yeast, Pencillium, Claviceps, Pleospora, Peziza Example of Basidiomycetes (Club fungi) Mushroom, toadstools, puffballs, stink horns, shelf fungi, racket fungi, rusts and smuts Example of Deuteromycetes (Fungi imperfecti) Alternaria, Fusarium, Collectrotrichum




Phylum Of Fungi Galvanologist Movieshdflix Site




Fungi Concepts Of Biology
Basidiomycota (club fungi) produce showy fruiting bodies that contain basidia in the form of clubs Spores are stored in the basidia Most familiar mushrooms belong to this division Deuteromycota (imperfect fungi) belong to a polyphyletic group that doesFungi are eukaryotic, like protists Habitat Club fungi live on dead and decaying plant matter What They Eat Club fungi's enzymes decompose wood, leaves, and other organic materials What Eats Them Mobility Club fungi can reproduce asexually, but sexual reproduction isAscomycota (sac fungi) may have unicellular or multicellular body structure;




It S A Perfect Year For Fungi Foragers If You Can Dodge The Killers Cropping Up In Woodlands Daily Mail Online




Eukaryotic Microorganisms Fungi Online Presentation
They are grouped under club fungi, a type of fungi that is a clubshaped structure What are examples of fungi?Features includes sexual spores in the basidiocarp (mushroom) and that they are mostly decomposersA feature is sexual spores in sacs (asci);



Sac
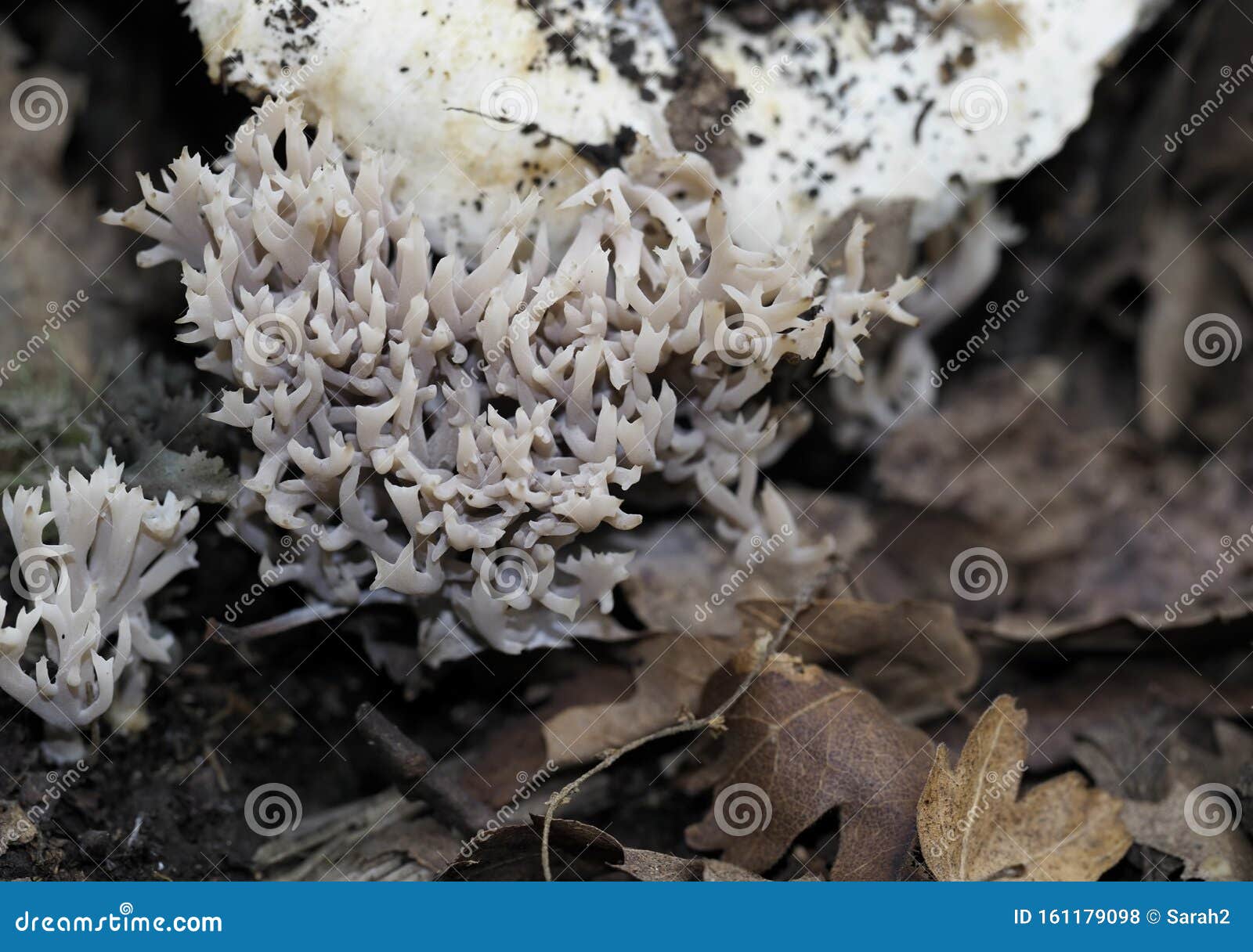




2 498 Basidiomycota Photos Free Royalty Free Stock Photos From Dreamstime
Basidiomycota (basidiomycetes or club fungi) Examples Mushrooms, bracket fungi, puffballs, rusts, smuts Sexual reproduction Basidiospores Deuteromycota (deuteromycetes or imperfect fungi) Examples Molds;C Candida albicans CandidiasisExamples include the yeasts used in bread, wine, and beer production Basidiomycota (club fungi) have multicellular bodies;




Exam Preparation Biology Study Material And Notes



Club Fungi King Of Kingdom S By Evan
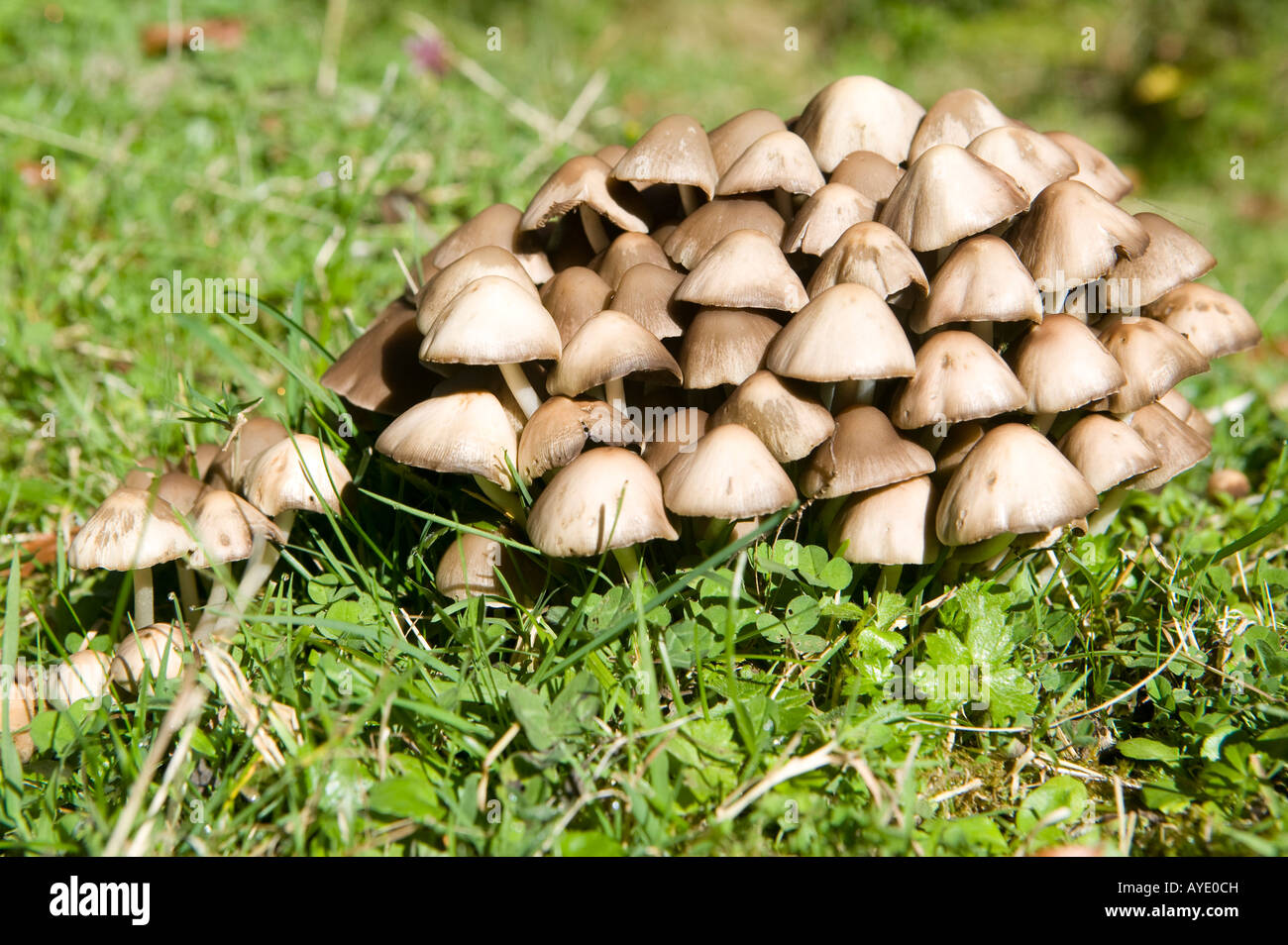
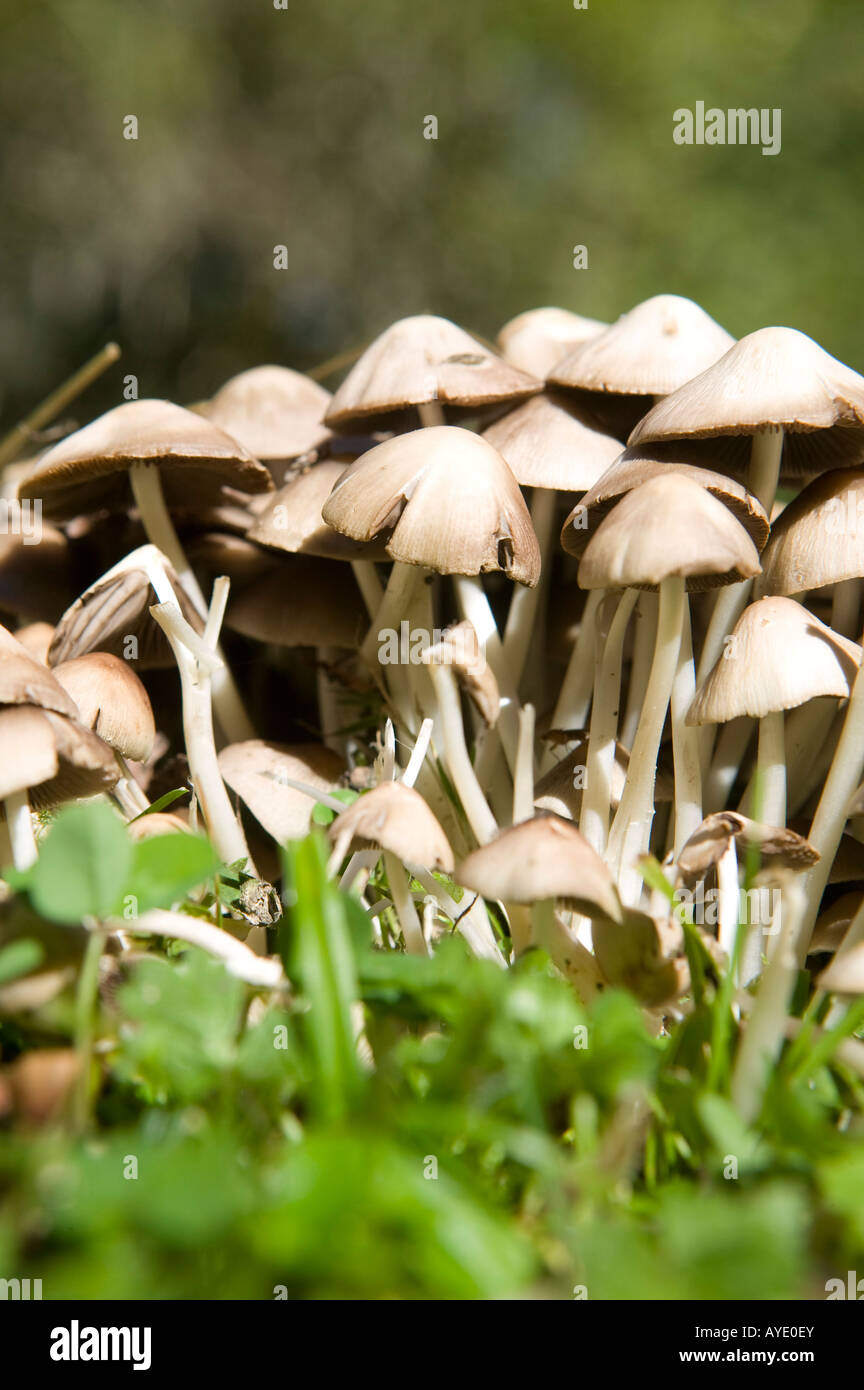
What are the spore cases on threadlike fungi called?sporangia 4 groups of fungi 1threadlike 2sac fungi 3club fungi 4imperfect fungi the largest group of fungi issac fungi some examples of sac fungi areyeasts, powdery mildews, truffles, and morels name two ways sac fungi are usefulExamples of Glomeromycota Although there aren't as many types of fungi in phylum Glomeromycota as other phyla in the fungi kingdom, they still play an important role in their terrestrial and wetland habitats Glomeromycetes form symbiotic relationships with their plant hosts, also known as arbuscular mycorrhizaeThe fungus provides nutrients to the plants, whichSome members the club fungi family



Fungi




Kingdom Fungi Continued
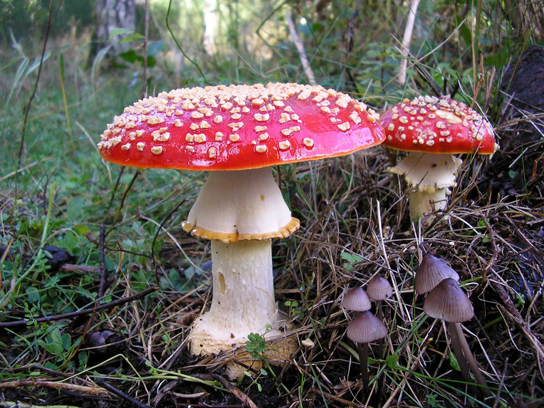
Classification are based on the following features Morphology and appearance of the fungus Morphology of reproductive structures Types of spores and method by which they are produced Nature of the life cycle Besides, physiological and biochemical features of The Arizona Mushroom Society, Inc, is a 501 (c) (3) taxexempt/taxdeductible nonprofit Arizona corporation, and is the state affiliate of the North American Mycological Association We offer a variety of forays, educational meetings, dinners, and other events designed to appeal to novices and experienced mushroom hunters alikeClub fungi species reproduce sexually by forming spores on top of clubshaped structures called basidia The club fungi are believed to be closely related to the sac fungi This large group includes species that are known as mushrooms, toadstools, earthstars, stinkhorns, puffballs, jelly fungi, coral fungi, and many other interesting names




The Club Fungi Powerpoint



2
Club fungi examples include rusts, shelf fungi, puffballs, toadstools, mushrooms sexual reproduction form basidium diploid spore mother cells at tips of basidia undergo meiosis to form haploid basidiospore basidiospores are released at maturity at tips of basidia human impact of basidiomycota decomposers Q6 State any two diseases caused by fungi Ans Candidiasis and Aspergillosis are two examples of fungal diseases Q7 Write 2 fungi examples with scientific names Ans Two examples of fungi along with the scientific names are Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and White button mushroom Agaricus bisporus Learn At EmbibeA feature is sexual spores in sacs (asci);




Mushroom Definition Characteristics Species Facts Britannica




Ascomycota Wikipedia
Trichophyton interdigidale Athletes foot or tinea pedis; The basidia is clubshaped, and basidiomycetes are also called club fungi Examples Agaricus (edible mushrooms), Puccinia (Rust fungi), Ustilago (Smut fungi), Polyporus (Bracket fungi), Candida etc Deuteromycetes (imperfect fungi) There are about 17,000 species of Deuteromycetes They only have asexual or vegetative stagesMany examples of copper, brass and silver jewelry designed by the Lapidary Club members There will be handson activity to make a textured copper pendant and earrings Wear closedtoe shoes and long pants Bring small jewelry pliers and a Sharpie pen if you have them Material fee of $ paid at class Instructor Lapidary Club




8 Fungi Ideas Fungi Stuffed Mushrooms Mushroom Fungi




Mushroom Observer Glossary Term Club Fungi
The fungi comprising the phylum Basidiomycota commonly are known as basidiomycetes It is a large phylum that includes forms commonly known as mushrooms, boletes, puffballs, earthstars, stinkhorns, birdsnest fungi, jelly fungi, bracket or shelf fungi, and rust and smut fungi Salient features Habit and habitat Both parasite and saprophyticAscomycota (sac fungi) may have unicellular or multicellular body structure;Features includes sexual spores in the basidiocarp (mushroom) and that they are mostly decomposers;




Biological Diversity 4




Basidiomycota Phylum Of Fungi Britannica
Phylum Basidiomycota (Club Fungi) Some examples of basidiomycetes are mushrooms, puffballs, shelf fungi, birds nest fungi, and stinkhorns This group includes some serious plant diseases such as rusts and smuts Mushrooms Shelf fungi are particularly important in breaking down wood A fungus is a member of a large group of organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and moulds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, and bacteriaThe discipline of biology devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycologyMycology has often been regarded as aKingdomFungi Phylum Basidiomycota Class Basidiomycetes Order Polyporales Family Meripilaceae Genus Rigidoporus Species Rigidoporus ulmarius




Bacteria Protists And Fungi Pdf Free Download




Basidiomycota Fungi And Deuteromycota Fungi Youtube
Examples are Collybia tuberosa with its appleseedshaped and coloured sclerotium, Dendrocollybia racemosa with its sclerotium and its Tilachlidiopsis racemosa conidia, Armillaria with their rhizomorphs, Hohenbuehelia with their Nematoctonus nematode infectious, state and the coffee leaf parasite, Mycena citricolor and its Decapitatus flavidus propagules called gemmaeThe Ascomycetes include fungi that cause chestnut blight and Dutch elm disease Claviceps purpurea is a parasite on rye grass that causes ergot Basidiomycota (club fungi) Basidiomycetes also possess septate hyphae The sexual spores, called basidiospores, are produced by a clubshaped structure called a basidium This phylum contributes fungi used to make beer, bread, cheese, and medicines Examples include Aspergillus and Penicillium Phylum Basidiomycota The club fungi, or basidiomycetes, belonging to the phylum Basidiomycota produce basidiospores on clubshaped structures called basidia The phylum includes most common mushrooms, smut fungi, and rust
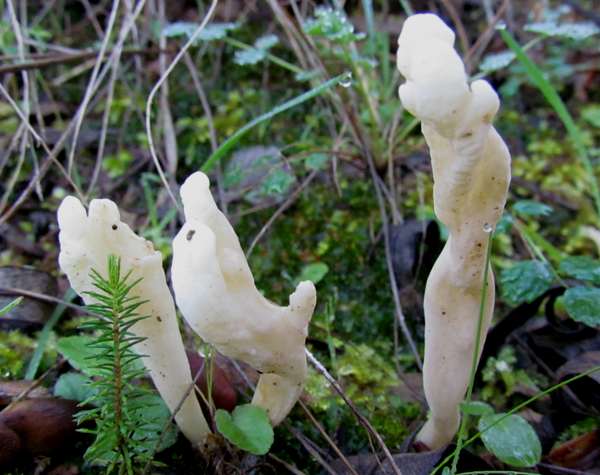




Clavulina Rugosa Wrinkled Club Fungus




Fungi Classification And Land Adaptations In Microbiology
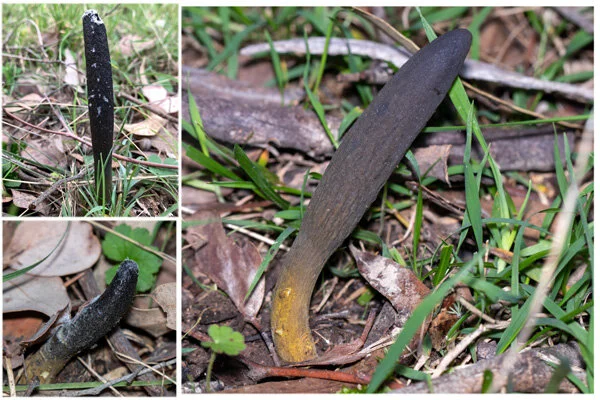
There are club fungi, sac fungi, zygote fungi, and imperfect fungi Members of the club fungi include?Fungi and algae) taken in the wild are suitable wildlife subjects, as are carcasses of extant species Images meeting the Wildlife Definition may be entered in Nature sections as well as Wildlife Sections Photojournalism Division Definition Photojournalism entries shall consist of images with informative content and emotional impactClubshaped mushrooms Toggle text A clubshaped mushroom is so named because its head is shaped like a club It can be hard to recognize as a mushroom, because its shape isn't as usual as the more familiar ball or capandstem mushrooms Some types of clubshaped mushrooms grow in clumps The swamp beacon, shown in this image, is a clubshaped fungus that is found in



Ascomycota




Biological Diversity 4




Club Fungi Group 6 Majela Fonseca Franco Figueroa Franco Figueroa Period 3 Mr Leon Biology Ppt Download




Green Lakes State Park Have You Ever Wondered How Mushrooms Pop Up In Your Yard So Quickly Mushrooms Are The Only Part Of A Fungus You Can See Above Ground Most




印刷可能 Club Fungi Club Fungi Meaning Gambarsaef26




Teaching The Fungal Tree Of Life Home




Fungus Wikipedia



Fungi Wallpapers Smashingwallpapers




Plant Plants Fungus Fungi Basidiomycetes Club Fungus Club Fungi Gill Fungus Gill Fungi Mushrooms Mottlegill Mottl Stock Photo Alamy




Fungi Concepts Of Biology




What Phylum Do Club Fungi Belong To Socratic



What Is The Difference Between Ascomycota And Basidiomycota Pediaa Com




Protists And Fungi By Brandon Howard



Basidiomycota




Basidiomycetes Pdf




Classification Of Fungi Phycomycetes Ascomycetes Basidiomycetes And Deuteromycetes




Mycelium The Future Is Fungi The Green Temple




Phylogenetic Relations Of Fungal Phyla Adapted From Bear Et Al 16 Download Scientific Diagram




Fascinating Fungi Introduction To The Kingdom Of Fungi And Tips For Getting Started With Recording Youtube




14 4 Phylum Basidiomycota Club Fungi 6 What Type Of Chegg Com




Plant Plants Fungus Fungi Basidiomycetes Club Fungus Club Fungi Gill Fungus Gill Fungi Mushrooms Mottlegill Mottl Stock Photo Alamy
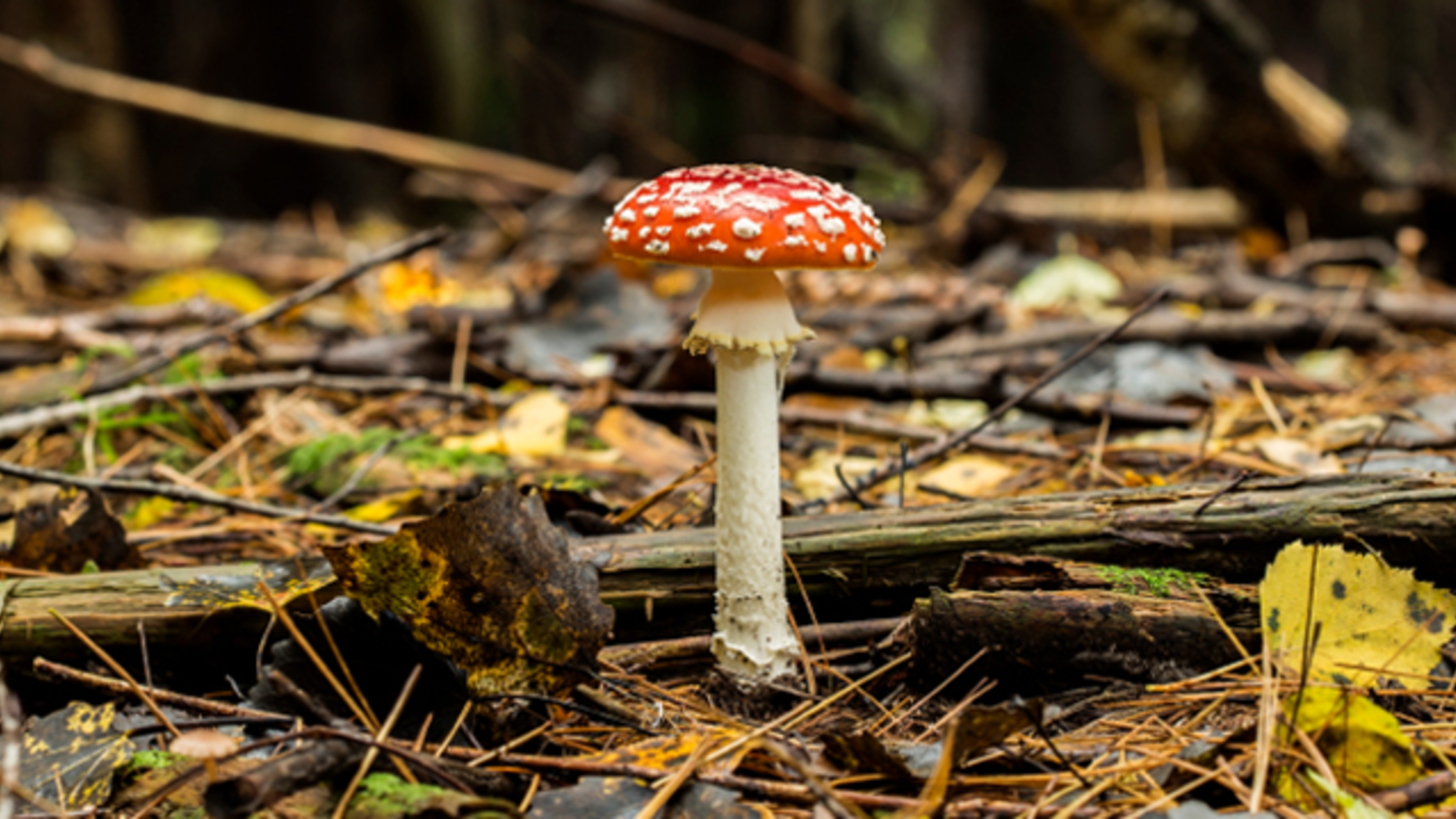




70 Totally Amazing Common Names For Fungi Mental Floss




Bacteria




Fungi Kingdom Mycology The Study Of Fungi Fungi Plural Fungus Singular 1 Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus 2 Heterotrophic They Do Not Make Their Ppt Download




Fungus Chapter Ppt Video Online Download




Basidiomycota Phylum Of Fungi Britannica



Fungi




Basidiomycota Advanced Ck 12 Foundation




Fungi Biology Shefalitayal
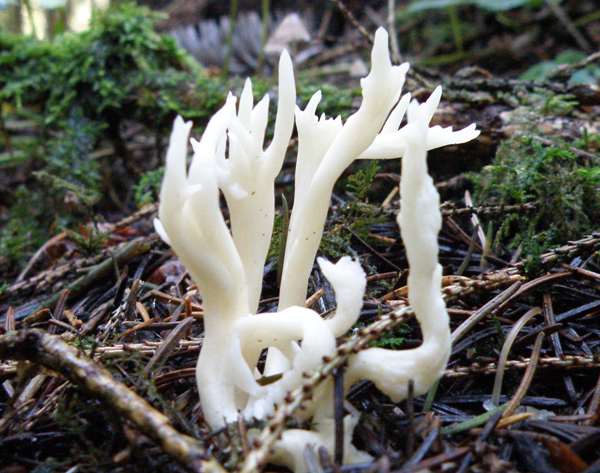




Clavulina Rugosa Wrinkled Club Fungus




Fungi Hunting Wonders Of Biology




Fungi Kingdom Mycology The Study Of Fungi Fungi Plural Fungus Singular 1 Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus 2 Heterotrophic They Do Not Make Their Ppt Powerpoint




Viruses Bacteria Protists Fungi Flashcards Quizlet




M O L L U S K S




Fungi




Ppt Chapter 21 Kingdom Fungi Notes Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Club Fungi Club Fungi




Fungi Hunting Wonders Of Biology




Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii



2



2



Teaching The Fungal Tree Of Life Home




Fungi Fungi With Club Shaped Parts That Produce Spores Called Club Fungi Mushroom Fungi Stuffed Mushrooms




Examples Of Fungi Phycomycetes Ascomycetes Basidiomycetes And Deuteromycetes




Mcqs On Kingdom Fungi By Biology Experts Notes Medium



Fungi




Discovering Fungi Field Studies Council




The Fungi Kingdom Mycology The Study Of Fungi
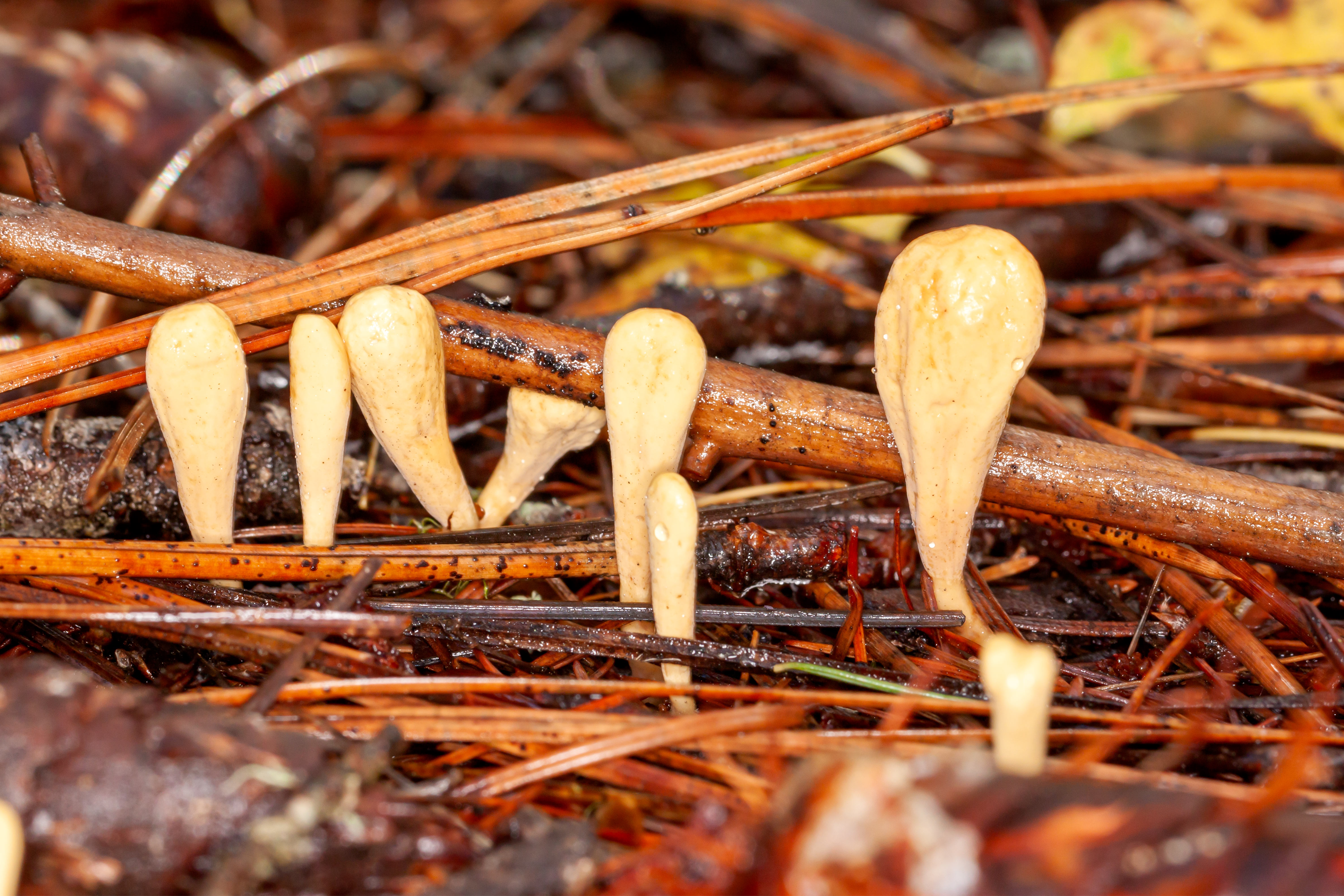




Mushroom Forms First Step To Fungi Identification Image Wildlife




Hillis2e Ch22
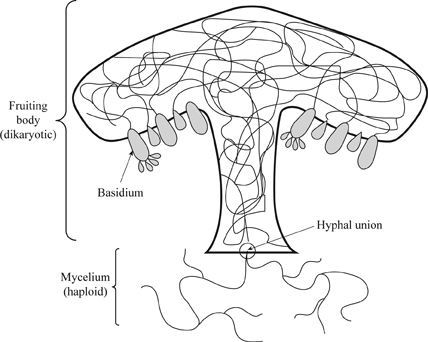



Definition Of The Major Groups Of Fungi Chegg Com



Club Fungi King Of Kingdoms



Club Fungi King Of Kingdoms



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes



Club Fungi




The Fungi Kingdom Ppt Video Online Download




Club Fungi Facts Club Mushroom Dk Find Out




Ppt Section 5 3 Kingdom Fungi Pgs 152 158 Powerpoint Presentation Id




Classification Of Fungi Into 5 Phyla Flow Chart With Examples
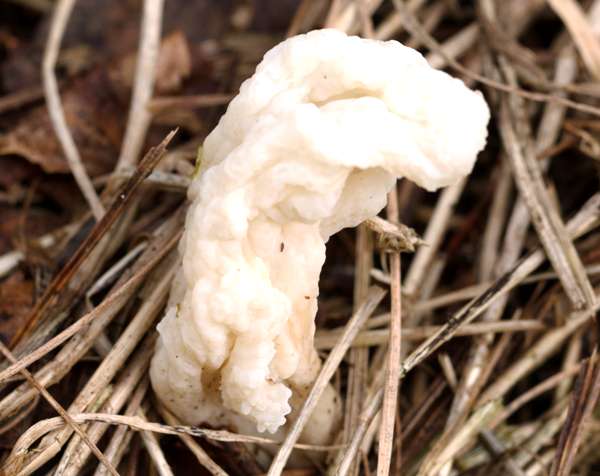




Clavulina Rugosa Wrinkled Club Fungus



Basidiomycota




Reading Fungi Biology Libretexts
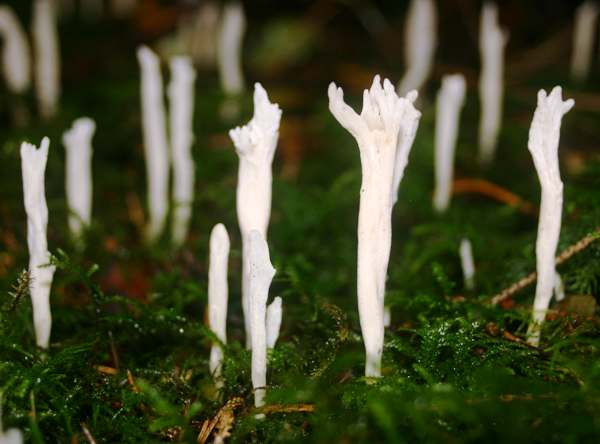




Clavulina Rugosa Wrinkled Club Fungus




Classification Of Fungi Drinvo




Fungi Lichens I Characteristics Of Fungi A What



Fungi Humans Examples Body Parasites Used Water Process Earth




Kingdom Fungi 1 Introduction To Fungi Mushrooms Toadstools




Ppt Club Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




The Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Flowering Plants 78 Steps Health




Is There A Fungus Among Us The Kingdom Fungi Fungi Are Not Plants They Are Eukaryotic Have Nucleus Heterotrophs Rely On Other Organisms For Food Ppt Download




16 3 Macrofungi Biology Libretexts
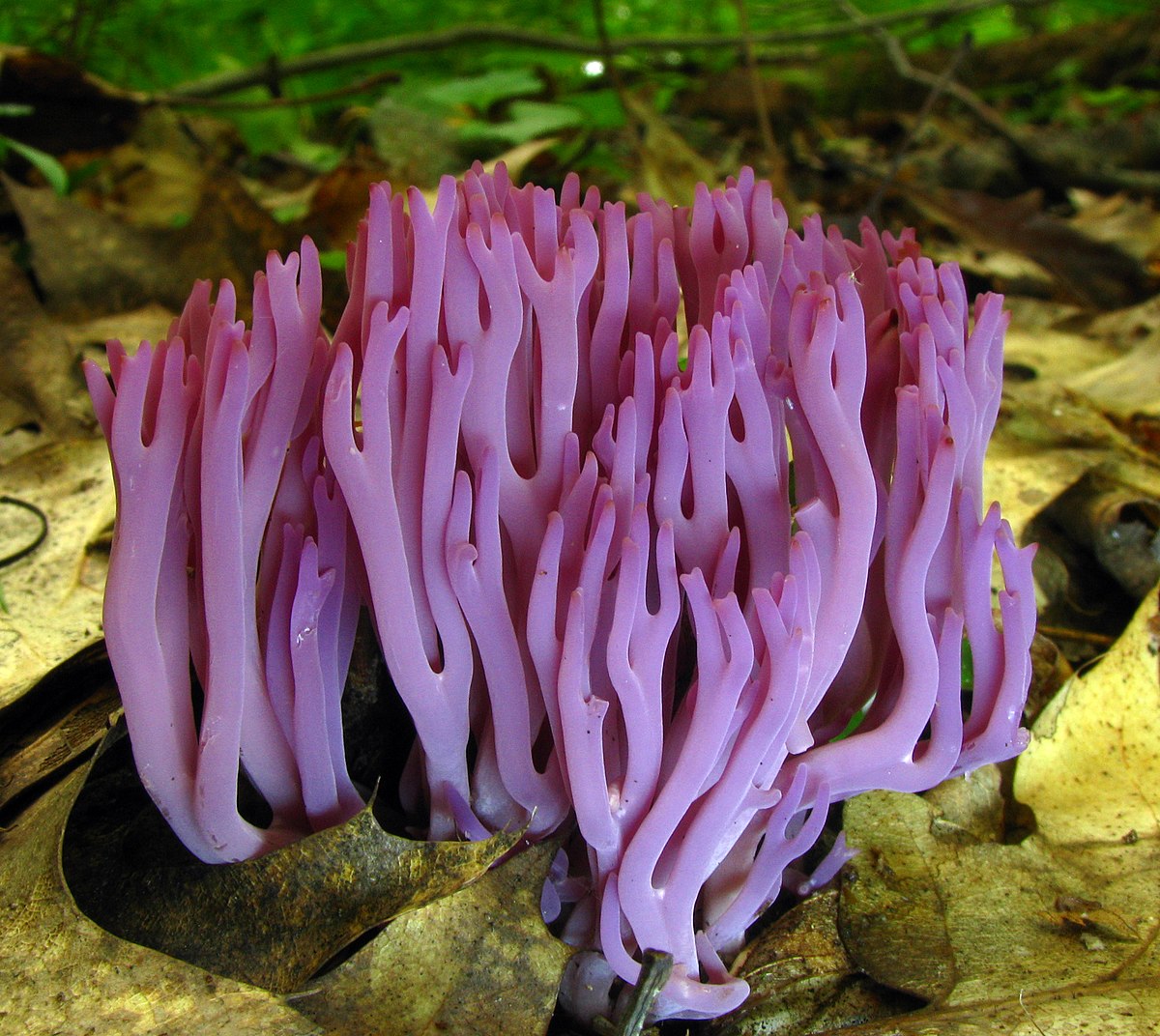




Clavarioid Fungi Wikipedia




Classifications Of Fungi Openstax Biology 2e




Which Genus Of Fungi Is In The Picture Trivia Questions Quizzclub




Ppt Chapter 21 Kingdom Fungi Notes Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



1



コメント
コメントを投稿